Direct carboxylation of simple arenes with CO2 through a rhodium-catalyzed C–H bond activation†
Abstract
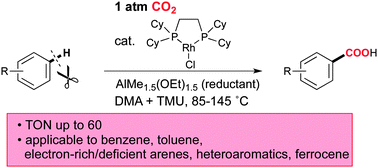
Direct carboxylation of simple arenes under atmospheric pressure of CO2 is achieved through a rhodium-catalyzed C–H bond activation without the assistance of a directing group. Various arenes such as benzene, toluene, xylene, electron-rich or electron-deficient benzene derivatives, and heteroaromatics are directly carboxylated with high TONs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...