A Hg(ii)-mediated “signal-on” electrochemical glutathione sensor†
Abstract
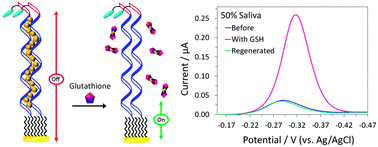
We report the design and fabrication of a DNA-based electrochemical sensor for detection of glutathione. Sensor signaling relies on glutathione's ability to chelate mercury Hg(II), displacing it from the thymine–Hg(II)–thymine complex formed between the surface-immobilized DNA probes. Our results show that this sensor is sensitive and selective enough to be employed in saliva.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...