The bifunctional regulation of interconnected Zn-incorporated ZrO2 nanoarrays in antibiosis and osteogenesis
Abstract
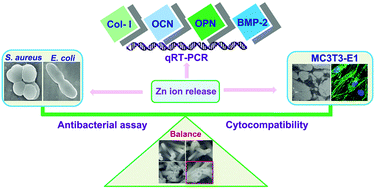
New generation biomaterials should be designed to bear long-term antibacterial activity, biocompatibility and even osteogenesis facilitation. In this study, the bifunctional regulation of antibiosis and osteogenesis is realized by the highly-ordered and interconnecting Zn-incorporated ZrO2 nanoarrays, which are prepared by a hydrothermal approach with the precursor hydrolyzed in situ and allow long-term controllable Zn release. The content of incorporated Zn can be easily controlled by pH of the HCl solution used for etching. All Zn-incorporated nanoarrays show good antibacterial properties against both Escherichia coli (E. coli, Gram-negative) and Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus, Gram-positive), as indicated by high antibacterial rates and the apparent inhibition zone. Analysis of the biocompatibility confirms that the hybrid nanoarrays could cause varying degrees of promotion for the adhesion and spreading of MC3T3-E1 cells. Zn incorporated ZrO2 nanotubes balance antibiosis and osteogenesis delicately, as proved by the up-regulated MTT and ALP activities, as well as the increase of bone-related gene expression (the mRNA level of OCN, OPN and BMP-2). The novel bone implant materials with better antibacterial properties can promote the osteogenesis, and have promising applications in biomedical devices and antibacterial control systems.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...