HPMC/PAA hybrid nanogels via aqueous-phase synthesis for controlled delivery of insulin
Abstract
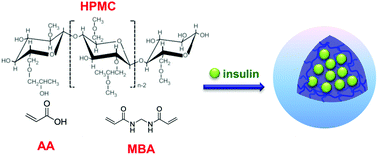
A facile controlled-release delivery system has been developed with hydroxypropylmethylcellulose/poly(acrylic acid) (HPMC/PAA) hybrid nanogels by surfactant-free polymerization in aqueous solution. The effect of temperature, reaction time, and amount of cross-linker on the size and morphology of the nanogels has been studied. The results showed that when the reaction temperature is higher than the lower critical solution temperature, the particle size increases with increasing temperature. And in a certain range, the particle size decreases with increasing reaction time and amount of cross-linker, the prepared nanogel under each condition being spherical. Thus, the HPMC/PAA hybrid nanogels were prepared at 41 °C for 4 h, and possessed a size ranging from 250 nm to 615 nm. Then, insulin was loaded into the nanogel, and the pH and temperature sensitivity of the nanogel was studied, the results indicating that the release behavior of the nanogel can be regulated by pH and temperature. Finally, in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice, insulin-loaded HPMC/PAA complex was able to maintain blood glucose concentration at a low level for the first week compared to a control group. Therefore, the nanogels have potential biological application as a long-term, sustained insulin delivery system.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...