The development, characterization, and cellular response of a novel electroactive nanostructured composite for electrical stimulation of neural cells
Abstract
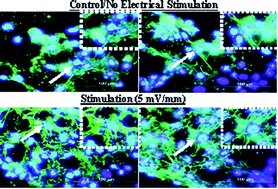
Electrical stimulation is a primary method to repair or restore neurological functions. In this regard, we describe the underlying strategy, chemical/structural design, and gifted attributes of a novel nanostructured electroactive composite electrode comprising organic (highly conducting polymer) and inorganic (carbon nanotubes) components. The electrode was characterized in terms of electrical properties, structure and neural cell response. First, the electrical probe is robust and characterized by low impedance, high charge injection capacity, and is biocompatible to facilitate cellular interactions. Second, the combination of in vitro experiments, fluorescence, and electron microscopy of electrically stimulated cells (NB-39-Nu human neuroblastoma cells) at different applied electric field strengths demonstrated that the electrochemically synthesized hybrid nanostructured coating is conducive to neurite growth. Third, the study on the effects of electrical field strength on protein synthesis and mechanism implied cell-to-cell communication based on the change in the regulation of endogenous cytoskeletal proteins, actin, vinculin, and fibronection involving cell mobility and cell adhesion. The cell-to-cell communication is of significant relevance to functional neuronal circuits in cell translational therapy. Taken together, the results also point to the potential of nanostructured composites for use as substrates to modulate cellular activity via electrical stimulation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...