One-step polymer screen-printing for microfluidic paper-based analytical device (μPAD) fabrication†
Abstract
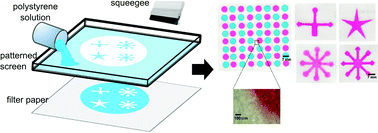
We report a simple, low-cost, one-step fabrication method for microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (μPAD) using only polystyrene and a patterned screen. The polystyrene solution applied through the screen penetrates through the paper, forming a three-dimensional hydrophobic barrier, defining a hydrophilic analysis zone. The optimal polystyrene concentration and paper types were first investigated. Adjusting polystyrene concentration allows for various types of paper to be used for successful device fabrication. Using an optimized polystyrene concentration with Whatman#4 filter paper, a linear relationship was found to exist between the design width and the printed width. The smallest hydrophilic channel and hydrophobic barrier that can be obtained are 670 ± 50 μm and 380 ± 40 μm, respectively. High device-to-device fabrication reproducibility was achieved yielding a relative standard deviation (%RSD) in the range of 1.12–2.54% (n = 64) of the measured diameter of the well-shaped fabricated test zones with a designed diameter of 5 and 7 mm. To demonstrate the significance of the fabricated μPAD, distance-based and well-based paper devices were constructed for the analysis of H2O2 and antioxidant activity, respectively. The analysis of H2O2 in real samples using distance-based measurement with CeO2 nanoparticles as the colorimetric agent produced the same results at 95% confidence level, as those obtained using KMnO4 titration. A proof-of-concept antioxidant activity determination based on the 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) assay was also demonstrated. The results verify that the polymer screen-printing method can be used as an alternative method for μPAD fabrication.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...