Gd–Al co-doped mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with Ru(bpy)32+ as a dual-modality probe for fluorescence and magnetic resonance imaging†
Abstract
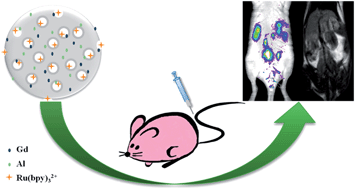
Mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) were co-doped with Gd3+ and Al3+ and then loaded with Ru(bpy)32+ by ion-exchange to prepare Ru/Gd–Al@MSNs. The as-prepared Ru/Gd–Al@MSNs were applied as contrast agents for in vivo fluorescence and magnetic resonance (MR) dual-modality imaging with a mouse as a model. The effects of Al3+ and MSNs on longitudinal relaxivity (r1) and fluorescence were investigated using a series of Gd-containing silica nanoparticles, including Gd@MSNs, Gd–Al@MSNs, and Ru/Gd–Al@nonporous silica nanoparticles. Co-doping with Al3+ improved the loading of Gd3+; the mesoporous structure improved the water exchange rate. The improvement enhanced the MR imaging efficiency of the Ru/Gd–Al@MSN probe. A higher relaxivity (19.2 mM−1 s−1) was observed compared to that from a commercial contrast agent, Gd-diethylene triamine pentaacetic acid (Gd-DTPA). Importantly, the mesoporous structure provided a large specific surface area for the loading of Ru(bpy)32+ by a simple ion-exchange procedure. Intense red fluorescence was observed from Ru/Gd–Al@MSN probes. The versatility of Ru/Gd–Al@MSNs for dual-modality imaging was demonstrated using in vivo fluorescence imaging and T1-weighted MR imaging with a mouse model. The nanoparticles are biocompatible and may be attractive for clinical applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...