Electrochemical analysis of the fibrillation of Parkinson's disease α-synuclein
Abstract
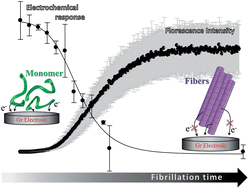
Amyloid formation of proteins and peptides is an important biomedical and biotechnological problem, intensively studied and yet not fully understood. In this context, the development of fast and reliable methods for real-time monitoring of protein misfolding is of particular importance for unambiguous establishment of disease-, drug- and environmentally induced mechanisms of protein aggregation. Here we show that the extent of aggregation of α-synuclein (αSN), involved in Parkinson's disease and other neurodegenerative disorders, can be electrochemically monitored by oxidizing tyrosine (Tyr) residues surface-exposed in monomeric αSN and buried in fibrillated αSN adsorbed onto graphite electrodes. Adsorption of αSN, analyzed through the Tyr electrochemistry, followed the Langmuir adsorption isotherm. The degree of electrooxidation of Tyr in αSN decreased upon protein fibrillation and correlated with the extent of αSN aggregation determined by the spectroscopic analysis of the fibrillation process. Minor changes in the adsorption state of αSN were followed through the shift of the Tyr oxidation potential, consistent with the compact and less-compact/unfolded conformation of αSN. Our results allow reliable electroanalysis of the extent of αSN fibrillation in vitro and offer an efficient tool for future in vivo monitoring of the protein conformational state.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...