Utilising non-consensus pathology measurements to improve the diagnosis of oesophageal cancer using a Raman spectroscopic probe
Abstract
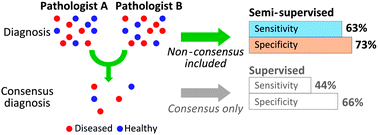
The application of semi-supervised methodology to improve the classification performance of a Raman spectroscopic probe for the diagnosis of oesophageal cancer is described. It is well known that gold standard histopathology diagnosis can be highly subjective, particularly for diseases which have several stages, such as cancer. A ‘consensus’ pathology decision can be obtained to ensure a robust gold standard by obtaining a diagnosis from several experts and samples are then only included in standard classification models if they have been assigned the same pathology by all experts. This can result in a significant number of samples that are excluded from the analysis as no consensus was reached. In this work semi-supervised methodology was used to extend Principal Component Analysis followed by Linear Discriminant Analysis (PCA-LDA) to incorporate samples without consensus pathology when discriminating between benign and oesophageal cancer specimens measured using a Raman endoscopic probe ex vivo. We demonstrate that a fully semi-supervised approach improved sensitivity and specificity from 73% and 78% (PCA-LDA) to 78% and 84% (semi-supervised) for discriminating between intestinal metaplasia and dysplasia and from 44% and 66% (PCA-LDA) to 63% and 72% (semi-supervised) when discriminating between intestinal metaplasia and low grade dysplasia.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...