Surface modification of silica nanoparticles using 4-aryloxy boron dipyrromethene (BODIPY) enhances skin permeation
Abstract
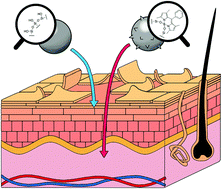
4-Aryloxy boron dipyrromethene (BODIPY) modification of the surface of silica nanoparticles (NPs) improved permeability through the membrane of HaCaT skin cells and swine skin tissue. The 35 nm BODIPY-modified NPs penetrated tape-stripped skin and reached the dermis within 1 h. Since these NPs can encapsulate a variety of molecules including macromolecules, they are expected to serve as effective carriers for the delivery of drugs, genes, and other compounds through skin and into cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...