A degradable polycyclic cross-linker for UV-curing nanoimprint lithography†
Abstract
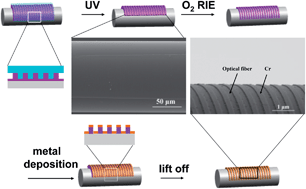
In this paper, we design and synthesize a degradable polycyclic diacrylate cross-linker, 2,10-diacryloyloxymethyl-1,4,9,12-tetraoxaspiro[4.2.4.2] tetradecane (DAMTT), from easily available starting materials by bis-ketalization of 1,4-cyclohexanedione with glycerol, followed by esterification with acryloyl choride. The chemical structure of the degradable cross-linker is characterized by FTIR, 1H NMR and GC-MS. A UV-NIL resist based on DAMTT has a very low shrinkage (about 2.5%) and a high Young's modulus of 1.89 GPa after UV-curing, and is soluble in acidic media. Patterns with sub-10 nm resolution are faithfully imprinted into the DAMTT film. The degradable cross-linker is incorporated with a multifunctional acrylated siloxane to increase O2 RIE resistance as an etch barrier for high aspect ratio pattern transfer. The cross-linked film of the UV-curable resist remains soluble in acidic media even though its formulation contains acrylated siloxane up to 50% (w/w). Moreover, in contrast to most UV-NIL resists which are insoluble in solvents after curing, the DAMTT resist can independently achieve a lift-off process without the assistance of a thermoplastic polymer layer. That makes it possible to fabricate metal nanostructures on highly curved surfaces via a hybrid UV-curing nanoimprint technique. For example, metal gratings are successfully fabricated on the cylindrical surface of an optical fiber via a lift-off process.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...