Enhanced charge extraction of polymer solar cell by solution-processable gold nanoparticles†
Abstract
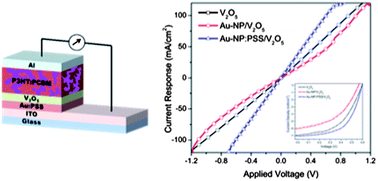
The utilization of metallic
* Corresponding authors
a
School of Chemical and Biomedical Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, 62 Nanyang Drive, Singapore 637459
E-mail:
tytan@ntu.edu.sg
Fax: +65 6794 7553
Tel: +65 6316 8829
b Globalfoundries Singapore Pte. Ltd, 60 Woodlands Industrial Park D, Street 2, Singapore 738406, Singapore
c
Institute for Clean Energy and Advanced Materials, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China
E-mail:
ecmli@swu.edu.cn
The utilization of metallic

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
S. Y. Khoo, H. Yang, Z. He, J. Miao, K. C. Leong, C. M. Li and T. T. Yang Tan, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2013, 1, 5402 DOI: 10.1039/C3TC30956H
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence. You can use material from this article in other publications without requesting further permissions from the RSC, provided that the correct acknowledgement is given.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
