Chemically tunable cationic polymer-bonded magnetic nanoparticles for gene magnetofection†
Abstract
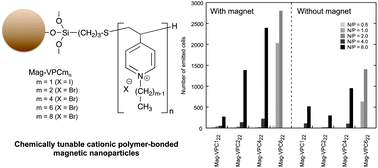
This study evaluates the efficiency of novel non-viral vectors consisting of super paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles functionalized with the chemically tunable cationic polymer for in vitro gene magnetofection. The cationic polymer, poly(vinyl pyridinium alkyl halide), with a reactive alkoxysilyl group at one terminal of the polymer (VPCmn, m = length of the side chain and n = polymerization degree), was grafted onto the surface of iron oxide nanoparticles through a silane coupling reaction. The VPCmn grafted-magnetic nanoparticles (Mag-VPCmn) were quaternized with various alkyl halides such as methyl iodide (m = 1), ethyl bromide (m = 2), butyl bromide (m = 4), hexyl bromide (m = 6) and octyl bromide (m = 8). Mag-VPCmn quaternized with a shorter alkyl chain (m = 1, 2, 4 and 6) were water dispersible, but that quaternized with a longer alkyl chain (m = 8) was precipitated in water. The surface of water dispersible Mag-VPCmns was positively charged in pH ranging from 2 to 11, and is stable for more than one month in this pH range. The complexes of Mag-VPCmns and nucleoside molecules with various N/P ratios were evaluated using gel electrophoresis, surface charge (ζ-potential) measurement, and particle size measurement. In vitro transfection experiments were assayed in human embryonic kidney 293 cells (HEK293 cells) using pmaxGFP plasmid as a reporter gene. Gene expression was found to be strongly influenced by the length of the side alkyl chains. Higher transfection efficiencies were observed with longer alkyl chains (C6 > C4 > C2 ≥ C1), indicating that hydrophobic side chains were effective in increasing the transfection efficiency.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...