Synthesis of electroactive mesoporous gold–organosilica nanocomposite materials via a sol–gel process with non-surfactant templates and the electroanalysis of ascorbic acid†
Abstract
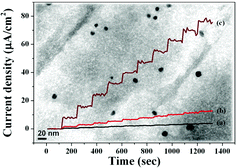
Electroactive mesoporous organosilica nanocomposites (EMONs) and electroactive mesoporous gold–organosilica nanocomposites (EMGONs) were successfully prepared in this work and were applied in ascorbic acid (AA) sensing. EMONs were synthesized by using an aniline pentamer (AP) as an electroactive segment which controlled the redox ability and influenced the degree of sensitivity of the nanocomposites towards AA. EMGONs were successfully prepared by a one-pot synthesis in HAuCl4 aqueous solution with different concentrations. Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) were selectively reduced on an AP segment in an EMON matrix, which acted as a reductant as well as providing a large surface area to absorb and react with chloroaurate anions (AuCl4−). The gold particle size can be controlled by varying the concentration of HAuCl4 (aq.), and distributed AuNPs with controllable size were fabricated for the EMGONs. A sensor constructed from an EMGON-modified carbon-paste electrode (CPE) demonstrated 21-fold and 6.3-fold higher electrocatalytic activity towards the oxidation of AA compared to those constructed using a bare CPE and EMON-modified CPE, respectively. The high surface area of the EMGON-modified CPE exhibited a good electrochemical response towards AA at a low oxidative potential with good stability and sensitivity and a wide linear analytical detection range.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...