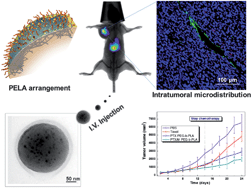
Various carriers are being advanced for anti-cancer therapy, which can protect drugs and ferry them to the target site. However, little understanding exists regarding the effect of molecular structure on anti-cancer drug delivery efficiency. To fill this knowledge gap, we take poly(lactic acid) (PLA), poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA), and poly-ethylene glycol-co-poly-lactide (PEG-b-PLA) polymers as prototype materials and comparatively explore the inherent relationship between the molecular structure and the delivery ability. Compared with PLA and PLGA NPs, PEG-b-PLA ones possess the advantages of longer blood circulation time, more tumor accumulation, and better intratumoral delivery ability. Subsequent mechanism investigations reveal that the molecular structure will regulate the polymer arrangement and render NPs different hydrophilicity/deformability, which dictate the distinct delivery performances. Finally, the superior PEG-b-PLA NPs are further loaded with the anti-cancer drug paclitaxel (PTX) and functionalized with magnetic (M) Fe3O4 nanocrystals. As-designed PTX/M PEG-b-PLA NPs show much better tumor inhibition efficacy and fewer side effects than the commercialized Taxol® formulation, strongly supporting their use as high-performance carriers for anti-cancer therapy.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...