Effect of interfacial dipoles on charge traps in organic–inorganic hybrid solar cells†
Abstract
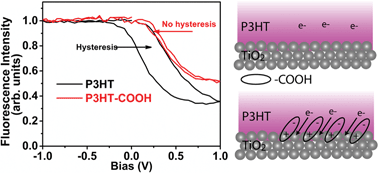
We introduce a bias-dependent fluorescence modulation technique to directly probe charge transfer processes at the organic–inorganic interface of working bilayer hybrid solar cells. Large hysteresis in bilayer P3HT–TiO2 devices indicates the presence of charge traps at the interface, unlike in P3HT-COOH–TiO2 devices. The results provide insights into enhancing interfacial interactions between organic and inorganic materials using modifiers such as –COOH, for the rational design of efficient hybrid solar cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...