Defect chemistry and lithium-ion migration in polymorphs of the cathode material Li2MnSiO4†
Abstract
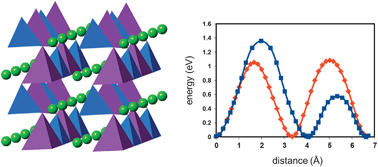
The search for new low-cost and safe cathodes for next-generation lithium batteries has led to increasing interest in silicate materials. Here, a systematic comparison of crystal properties, defect chemistry and Li-ion migration behaviour of four polymorphs of Li2MnSiO4 is reported based on the results of atomistic simulations. The four polymorphs examined have Pmn21, Pmnb, P21/n, and Pn symmetry. Lattice energies of all four polymorphs are very similar, with only a small energy preference for the two orthorhombic phases over the monoclinic phases, which explains the difficulty experimentalists have had preparing pure-phase samples. Defect formation energies of the polymorphs are also similar, with antisite Li/Mn defects the most energetically favourable. Detailed analysis of the Li-ion migration energy surfaces reveals high

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...