Room-temperature proton transport and its effect on thermopower in a solid ionic semiconductor, TTFCOONH4†
Abstract
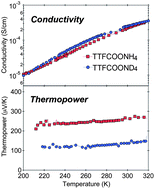
Ammonium proton in a solid ionic semiconductor, TTFCOONH4, is shown to be mobile under anhydrous conditions at room temperature by the hydrogen concentration cell method. Isotope substituted TTFCOOND4 exhibits a 2.2 H/D isotope effect in ion carrier mobility with TTFCOONH4. First-principles calculations reveal that an efficient proton-transfer pathway via low-barrier N⋯H+⋯N hydrogen bonds reduces the activation energy to 0.12 eV, which is quite small and comparable to that reported in a bulk water system. The ac conductivity of TTFCOONH4 and TTFCOOND4 is similar at room temperature, reflecting similar hole carrier concentrations. In sharp contrast, the thermopower exhibits a large isotope effect: TTFCOONH4 shows 260 μV K−1, which is twice as large as that predicted by the hole carrier concentration and the value of TTFCOOND4, with 138 μV K−1. The 1.9 H/D isotope effect in thermopower closely relates to the 2.2 H/D isotope effect in ion carrier mobility. Proton carriers in the temperature gradient enhance thermopower without cancelling out the effect of holes in the solid state owing to possession of the same positive charge.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...