Flow-controlled densification and anomalous dispersion of E. coli through a constriction†
Abstract
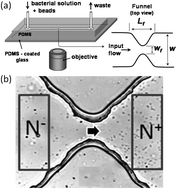
Dispersion and migration of bacteria under flow in tortuous and confined structures such as porous or fractured materials is related to a large spectrum of practical interest, but is still poorly understood. Here, we address the question of transport and dispersion of an E. coli suspension flowing through a micro-fluidic channel with a funnel-like constriction in its center. We show a counter-intuitive symmetry breaking of the bacterial concentration, which increases significantly past the funnel. This concentration enhancement persists over large distances from the funnel and disappears at large flow rate values. We map our results onto a one dimensional convection–diffusion equation predicting quantitatively the experimental results, without free parameters, when a conservative non-local source term is introduced. This last term, measured experimentally, represents a long range memory effect due to the unbalance of wall

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...