Experimental investigation of the mechanical grinding effect on graphene structure
Abstract
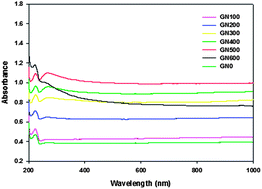
Graphene has been proven to be a promising material for various applications due to its outstanding chemical, physical, optical as well as mechanical properties. To further improve these properties of graphene, here we apply a grinding method with various speeds (100–600 rpm) of a planetary ball mill under wet conditions in graphene based aqueous solution. Therefore, the improvements in dispersion and thermal characteristics of the graphene–water solution were investigated based on the morphological and structural changes. The best dispersibility and highest thermal conductivity of graphene–water solution were observed for a grinding speed of 500 rpm. As a result, the grinding speed of 500 rpm is found as the optimum condition of planetary ball milling in the case study. The reason for the grinding speed of 500 rpm revealing the best condition is attributed to the reduced ratio (ID/IG = 0.221) of the D band and the G band in Raman spectroscopy. We believe that structurally upgraded graphene in this study would greatly improve the performance of the graphene based devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...