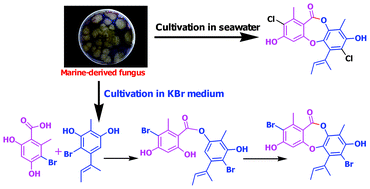
Directed biosynthesis through biohalogenation of depsidones was conducted by cultivating the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus unguis in media containing different halogen salts (i.e., KBr, KI, and KF). The fungus grown in a KBr medium produced new brominated unnatural natural depsidones, while those cultured in KI produced non-halogenated depsidone, unguinol, as a major metabolite. Unexpectedly, the directed biosynthesis through biohalogenation provides insights into depsidone biosynthesis; particular biosynthetic intermediates were co-isolated with brominated depsidones from the fungus cultured in KBr medium. These biosynthetic congeners support that the depsidone biosynthesis in A. unguis operates through the oxidative coupling of depsides, not through the benzophenone-grisadienedione pathway. The isolated depsidones inhibited aromatase, a therapeutic target for the treatment of breast cancer.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...