Investigation of quantitative structure–reactivity relationships in the aliphatic Claisen rearrangement of bis-vinyl ethers reveals a dipolar, dissociative mechanism†
Abstract
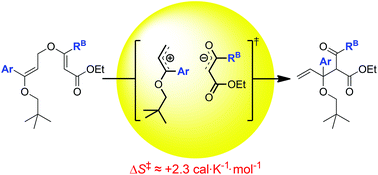
Kinetic investigations of substituent effects in the thermal rearrangement of bis-vinyl ether substrates are reported. Findings indicate that the influence of the various substituent patterns on the rate of rearrangement in these compounds differs from that documented in the literature for the analogous [3,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement of allyl vinyl ethers. In addition, the thermochemical data collected suggests the existence of a dissociative transition state with significant dipolar character. These findings provide a unique contribution to the already extensive body of literature dedicated to mechanistic investigation of the Claisen rearrangement of aliphatic allyl vinyl ethers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...