An on-demand four-way junction DNAzyme nanoswitch driven by inosine-based partial strand displacement†
Abstract
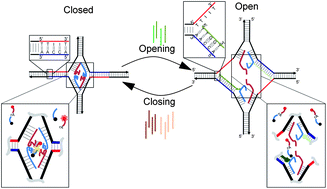
A DNA four-way junction device capable of junction expansion and contraction cycles using an inosine-based partial strand displacement scheme is reported. These nanoscale positioning capabilities are used to provide on-demand activation and deactivation of a pair of split E6 DNAzymes on the device. The device also demonstrates a combined catalytic rate significantly higher than the original E6 DNAzyme under similar operational conditions. This approach can provide structural organization and spatially control other multicomponent molecular complexes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...