Resistive switching in iron-oxide-filled carbon nanotubes†
Abstract
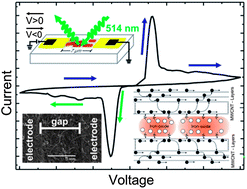
Iron-oxide-filled carbon nanotubes exhibit an intriguing charge bipolarization behavior which allows the material to be applied in resistive memory devices. Raman analysis conducted with an electric field applied in situ shows the Kohn anomalies and a strong modification of the electronic properties related to the applied voltage intensity. In addition, the ID/IG ratio indicated the reversibility of this process. The electrical characterization indicated an electronic transport governed by two main kinds of charge hopping, one between the filling and the nanotube and the other between the nanotube shells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...