Bio-inspired antireflective hetero-nanojunctions with enhanced photoactivity†
Abstract
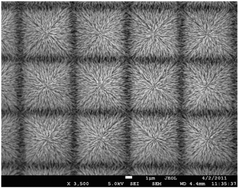
A bio-inspired antireflective hetero-nanojunction structure has been fabricated by the hydrothermal growth of ZnO nanorods on silicon micro-pyramids. It has been shown that this structure suppresses light reflection more effectively resulting in a high photocurrent response and good charge separation simultaneously. The strategy provides a means to enhance solar energy conversion.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...