Impairments of cells and genomic DNA by environmentally transformed engineered nanomaterials†
Abstract
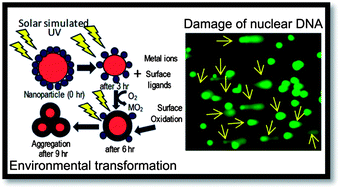
Enormous increase in the production of nanomaterials and their growing applications in the device technology, biotechnology and biomedical areas suggest the need for developing models for predicting the environmental health and safety (EHS) risks posed by such nanomaterials. We hypothesize that CdSe

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...