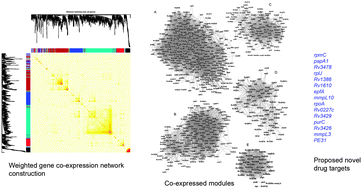
We have carried out weighted gene co-expression network analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to gain insights into gene expression architecture during log phase growth. The differentially expressed genes between at least one pair of 11 different M. tuberculosis strains as source of biological variability were used for co-expression network analysis. This data included genes with highest coefficient of variation in expression. Five distinct modules were identified using topological overlap based clustering. All the modules together showed significant enrichment in biological processes: fatty acid biosynthesis, cell membrane, intracellular membrane bound organelle, DNA replication, Quinone biosynthesis, cell shape and peptidoglycan biosynthesis, ribosome and structural constituents of ribosome and transposition. We then extracted the co-expressed connections which were supported either by transcriptional regulatory network or STRING database or high edge weight of topological overlap. The genes trpC, nadC, pitA, Rv3404c, atpA, pknA, Rv0996, purB, Rv2106 and Rv0796 emerged as top hub genes. After overlaying this network on the iNJ661 metabolic network, the reactions catalyzed by 15 highly connected metabolic genes were knocked down in silico and evaluated by Flux Balance Analysis. The results showed that in 12 out of 15 cases, in 11 more than 50% of reactions catalyzed by genes connected through co-expressed connections also had altered fluxes. The modules ‘Turquoise’, ‘Blue’ and ‘Red’ also showed enrichment in essential genes. We could map 152 of the previously known or proposed drug targets in these modules and identified 15 new potential drug targets based on their high degree of co-expressed connections and strong correlation with module eigengenes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...