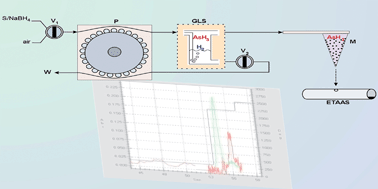
Arsenic determination in natural waters is an issue of current research. This article reports a novel hydride generation (HG) approach developed for As determination with electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry (ETAAS) detection. The HG process was interfaced with ETAAS through hydride trapping onto a carbon nanotubes microcolumn. To this end a homemade gas–liquid separator was used, allowing arsine formation and its flow throughout the CNT microcolumn. The retention process involved thus a solid phase extraction from the gas phase to the solid support. Once arsine generation was completed, the elution was carried out with nitric acid directly onto the dosing hole of the graphite furnace. Outstanding sensitivity with detection limit of 1 ng L−1, quantification limit of 5 ng L−1 and the characteristic mass, 5.8 ± 0.4 pg could be achieved. A satisfactory correlation between concentration of As and absorbance (R = 0.9993) from the limit of quantification up to 500 ng L−1, with a relative standard deviation of 6.3% were obtained. A sensitive enhancement factor of 38 was reached when 2 mL of sample were processed and 50 μL of HNO3 were used as eluent. The system was successfully applied to the analysis of a standard reference material, QC LL2 metals in natural waters. In addition tap water analysis provided an As concentration of 0.29 ± 0.03 μg L−1.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...