Amino acids and proteins at ZnO–water interfaces in molecular dynamics simulations†
Abstract
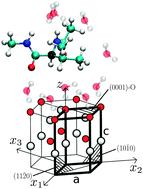
We determine potentials of the mean force for interactions of amino acids with four common surfaces of ZnO in aqueous solutions. The method involves all-atom molecular dynamics simulations combined with the umbrella sampling technique. The profiled nature of the density of water with the strongly adsorbed first layer affects the approach of amino acids to the surface and generates either repulsion or weak binding. The largest binding energy is found for tyrosine interacting with the surface in which the Zn ions are at the top. It is equal to 7 kJ mol−1 which is comparable to that of the hydrogen bonds in a protein. This makes the adsorption of amino acids onto the ZnO surface much weaker than onto the well studied surface of gold. Under vacuum, binding energies are more than 40 times stronger (for one of the surfaces). The precise manner in which water molecules interact with a given surface influences the binding energies in a way that depends on the surface. Among the four considered surfaces the one with Zn at the top is recognized as binding almost all amino acids with an average binding energy of 2.60 kJ mol−1. Another (O at the top) is non-binding for most amino acids. For binding situations the average energy is 0.66 kJ mol−1. The remaining two surfaces bind nearly as many amino acids as they do not and the average binding energies are 1.46 and 1.22 kJ mol−1. For all of the surfaces the binding energies vary between amino acids significantly: the dispersion in the range of 68–154% of the mean. A small protein is shown to adsorb onto ZnO only intermittently and with only a small deformation. Various adsorption events lead to different patterns in mobilities of amino acids within the protein.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...