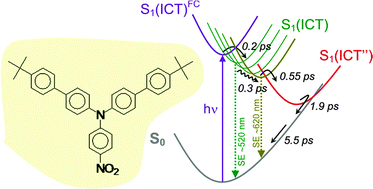
A series of emitting push–pull triarylamine derivatives, models of their widely used homologues in photonics and organic electronics, was investigated by steady-state and time-resolved spectroscopy. Their structural originality stems from the sole change of the electron-withdrawing substituent X (–H: 1, –CN: 2, –NO2: 3, –CHC(CN)2: 4), giving rise to efficient emission tuning from blue to red upon increasing the X electron-withdrawing character. All compounds are highly fluorescent in alkanes. The more polar compounds 2–4 undergo considerable Stokes shift and emission quenching in polar solvents. Femtosecond transient absorption data allowed us to identify the nature of the emissive state which varies as a function of the compound and surrounding polarity. A long-lived ππ* excited state with weak charge transfer character was found for 1. This excited state evolves into a long-lived ICT state with red-shifted emission for 2 in polar solvents. For 3 and 4, the ICT state is directly populated in all solvents. Long-lived and emissive in n-hexane, it relaxes in toluene to a new ICT′ conformation with stronger charge transfer character and enhanced Stokes shift. In more polar THF, ethanol, and nitrile solvents, ICT relaxes to a dark excited state ICT′′ with viscosity-dependent kinetics (<10 ps). The ICT′′ state lifetime drops with increasing solvent polarity (150 ps for 3 in THF, 8.5 ps in butyronitrile, 1.9 ps in acetonitrile), denoting an efficient radiationless deactivation to the ground state (back charge transfer). This result reveals a very small S0–S1 energy gap at the relaxed ICT′′ geometry, with a possible close-lying S0–S1 conical intersection, which suggests that the ICT → ICT′′ process results from a structural change involving a large-amplitude molecular distortion. This fast structural change can account for the strong fluorescence quenching observed for 3 and 4 in polar solvents. Finally, the magnitude of intersystem crossing between the singlet and triplet excited states largely depends on the electron-deficient X unit and the solvent itself. These observations help one conclude on the prevailing role played by the electron-withdrawing groups and the surrounding polarity in the photophysical performances of triphenylamine derivatives, largely employed in numerous emissive solid-state devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...