Tetra-primer ARMS-PCR is an efficient SNP genotyping method: An example from SIRT2
Abstract
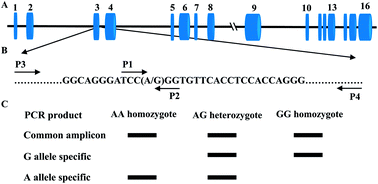
Tetra-primer amplification refractory mutation system PCR (T-ARMS-PCR) offers fast detection and extreme simplicity at a negligible cost for SNP genotyping. SIRT2, the family member (sirtuins, SIRT1-7) with the greatest homology to the silent information regulator 2 (Sir2), is the most abundantly expressed sirtuins in adipocytes and has been implicated in promoting fatty acid oxidation (FAO) by deacetylating various substrates. In the current study, we have successfully genotyped a new identified bovine SIRT2 SNP g.4140A > G by T-ARMS-PCR method and validated the accuracy by PCR-RFLP assay using 1255 animals representing the five main Chinese breeds. The concordance between the two different methods was 98.8%. Individuals with discordant genotypes were retyped by direct DNA sequencing. 40% of the discrepancies could be attributed to incomplete digestion in the PCR-RFLP assay. 60% of discordant genotypes resulted from allele failure in the T-ARMS-PCR assay. Chi-square test shows that the frequencies of SNP g.4140A > G are in Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium in all the samples (P > 0.05), which suggested that the five populations are almost a dynamic equilibrium even in artificial selection. Association analysis showed that the g.4140A > G polymorphism is significantly related to 24 months-old body weight in Nanyang cattle. Our results provide direct evidence that T-ARMS-PCR is a rapid, reliable, and cost-effective method for SNP genotyping and g.4140A > G polymorphism in bovine SIRT2 is associated with growth efficiency traits. These findings may be used for marker-assisted selection and management in feedlot cattle.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...