Effective separation and simultaneous determination of cefamandole and probenecid in body fluids by capillary zone electrophoresis with salicylic acid as an internal standard
Abstract
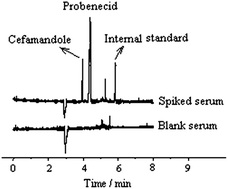
The applicability of capillary zone electrophoresis for the simultaneous determination of cefamandole and probenecid in body fluids has been studied using salicylic acid as an internal standard. A 10 mM disodium tetraborate solution (pH 8.0) was used as a running buffer and the UV wavelength was set at 230 nm for monitoring the analytes at a separation voltage of 18 kV. Under the optimized conditions, the analytes can be effectively separated in 6 min. The standard curves of cefamandole and probenecid showed good linearity in the range of 10–200 and 5–110 μg mL−1, respectively, with correlation coefficients r > 0.999. The detection limits (S/N = 3) of cefamandole and probenecid were 2.7 and 1.1 μg mL−1, respectively. Intra- and inter-day analytical precisions (relative standard deviation, RSD) of peak area and migration time for the two medicines were both less than 2%. The recoveries at three spiked levels of cefamandole and probenecid from urine and serum samples were in the range of 96.23–105.1% with RSD values of 0.55–2.36%. The proposed method was tested for clinical application by the simultaneous determination of cefamandole and probenecid in human urine and serum with satisfactory results.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...