A robust and simple-to-design multiplex DNA methylation assay based on MS-MLPA-CE-SSCP†
Abstract
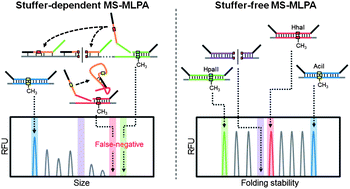
Aberrant DNA methylation is a potential diagnostic marker for complex diseases, such as cancer. With the increase in the number of genes known to exhibit disease-associated aberrant methylation, the need for accurate multiplex assays for quantifying DNA methylation has increased. Methylation-specific multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MS-MLPA) is one method that has been highlighted in this context. However, two limitations make the custom design of MS-MLPA assays impractical: the need for long probes containing stuffer sequences and a reliance on only one restriction enzyme. Here, we developed a variation of MS-MLPA that employs a simpler probe-design process. To overcome the above-mentioned limitations, we used stuffer-free MS-MLPA probes that are subsequently analyzed using high-resolution capillary electrophoresis-based single-strand conformational polymorphism (CE-SSCP) instead of conventional length-dependent CE. Moreover, multiple methylation-sensitive restriction enzymes (HhaI, HpaII, and AciI) were used simultaneously; thus, probes satisfying desired criteria were available for all targets. Using this assay concept, we analyzed 17 genes associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. Our results showed that the custom-designed assay based on MS-MLPA-CE-SSCP provided robust multiplex quantification of DNA methylation levels.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...