An aptasensor for electrochemical detection of tumor necrosis factor in human blood†
Abstract
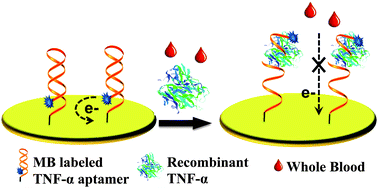
Electrochemical aptasensors can detect disease markers such as cytokines to provide point-of-care diagnosis that is low-cost, rapid, specific and sensitive. Herein, we describe the development of an aptamer-based electrochemical sensor for detection and analysis of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) – a key inflammatory cytokine – in whole human blood. When testing spiked blood, a TNF-α detection limit of 58 pM (10 ng mL−1) and a linear range of 6 nM (100 ng mL−1) could be achieved. Furthermore, detection of TNF-α in

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...