Crosslinked PEG mats for peptide immobilization and stem cell adhesion†
Abstract
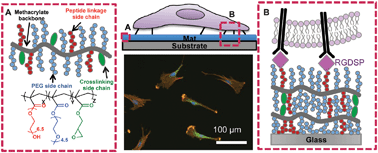
We have designed a lightly crosslinked PEG based copolymer coating with compositional flexibility as well as extended stability for studying human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs). Copolymers contain a majority of poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate (PEGMEMA) as a cytophobic background with poly(ethylene glycol) methacrylate (PEGMA) for peptide coupling, and less than 10% glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) for crosslinking. Copolymer thin films were crosslinked into 30 nm thick mats by either thermal treatment or ultraviolet light and were stable for 35 days in water at 37 °C. The amount of PEGMA in the copolymer was optimized to ∼11% to minimize non-specific cell–protein interactions while maximizing the amount of total bound peptides. Following the binding of RGDSP to the mat, hMSCs were seeded. The hMSC adhesion, spreading and focal adhesion complex formation were promoted in a concentration dependent manner. Mats coupled with a non-adhesive scramble (RDGSP) maintained their cytophobicity. Competitive detachment experiments further demonstrated that cell adhesion was mediated by receptor binding to the RGDSP peptide. Cell culture experiments performed at 1 and 2 weeks show that mats can still resist cell adhesion after incubation in a serum containing medium. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was effectively used to quantify the average total peptide concentration as 12.6 ± 6.14 pmol cm−2. A square 2.2 mm N (1s) element map shows an average value of 17.9 pmol cm−2 of RGDSP, which correlates well with the multipoint high resolution data. The stability of the copolymer, compositional flexibility, ease of application and the ability to precisely quantify bound peptides on the mats make these materials ideal for the study of cellular processes, where stability, functionality and topography of the biointerface are relevant.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...