AC electrophoresis of microdroplets in anisotropic liquids: transport, assembling and reaction†
Abstract
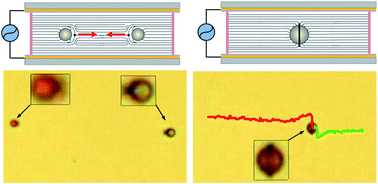
We describe the realization and controlled transport of water-based microreactors dispersed in a nematic liquid crystal and transported by application of an alternating electric field through the mechanism of induced charge

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...