Rewritable and shape-memory soft matter with dynamically tunable microchannel geometry in a biological temperature range†
Abstract
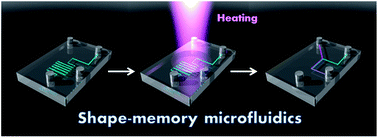
Here we present on-demand switchable microchip materials that display potent rewritable and shape-memory properties which are shown to contribute to fluidic control as pumps and valves. Semi-crystalline poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) was chemically crosslinked to show shape-memory effects over its melting temperature (Tm) because the crosslinking points set the permanent shape and the crystalline domains serve as thermally reversible

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...