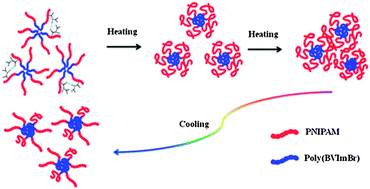
The assembly properties, thermal phase behavior and microdynamics of poly(NIPAM-b-BVImBr), poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-b-poly(1-butyl-3-vinylimidazolium bromide), in aqueous solution are investigated by dynamic light scattering (DLS), turbidity measurements and FTIR spectroscopy in combination with two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy (2Dcos) and the perturbation correlation moving window (PCMW) technique. In particular, the influence of the introduction of the poly(BVImBr) segment on the solution properties of the block copolymer has attracted our attention: a core–shell micelle structure forms, consisting of a relatively hydrophobic core of poly(BVImBr) and a hydrophilic shell of PNIPAM; the phase transition temperature increases, due to one more step in the dehydration process originating from the alkyl side chains of the poly(1-butyl-3-vinylimidazolium bromide) (PIL) segment; what's more, a stronger hysteresis during the heating–cooling cycle, closely related to the recovery process, is observed. It reveals that the hydrogen bonds of C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O⋯D–N among the micelles formed during heating are harder to remove, thus, the reconstruction of the C
O⋯D–N among the micelles formed during heating are harder to remove, thus, the reconstruction of the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O⋯D–O–D hydrogen bonding and the recovery hydration process for the C–H groups during cooling are prevented due to the compact and regular micelle structure. More interestingly, the C
O⋯D–O–D hydrogen bonding and the recovery hydration process for the C–H groups during cooling are prevented due to the compact and regular micelle structure. More interestingly, the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O groups interact with the N–D groups at room temperature because of the existence of the micelle structure, which is regarded as intra-micelle hydrogen bonding; above the LCST, hydrogen bonds of the C
O groups interact with the N–D groups at room temperature because of the existence of the micelle structure, which is regarded as intra-micelle hydrogen bonding; above the LCST, hydrogen bonds of the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O⋯D–N among the aggregated micelles called inter-micelle hydrogen bonding occur.
O⋯D–N among the aggregated micelles called inter-micelle hydrogen bonding occur.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O⋯D–N among the micelles formed during heating are harder to remove, thus, the reconstruction of the C
O⋯D–N among the micelles formed during heating are harder to remove, thus, the reconstruction of the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O⋯D–O–D hydrogen bonding and the recovery hydration process for the C–H groups during cooling are prevented due to the compact and regular micelle structure. More interestingly, the C
O⋯D–O–D hydrogen bonding and the recovery hydration process for the C–H groups during cooling are prevented due to the compact and regular micelle structure. More interestingly, the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O groups interact with the N–D groups at room temperature because of the existence of the micelle structure, which is regarded as intra-micelle hydrogen bonding; above the LCST, hydrogen bonds of the C
O groups interact with the N–D groups at room temperature because of the existence of the micelle structure, which is regarded as intra-micelle hydrogen bonding; above the LCST, hydrogen bonds of the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O⋯D–N among the aggregated micelles called inter-micelle hydrogen bonding occur.
O⋯D–N among the aggregated micelles called inter-micelle hydrogen bonding occur.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...