How is the anionic tetrahedral intermediate involved in the isomerization of aspartyl peptides to iso-aspartyl ones? A DFT study on the tetra-peptide†
Abstract
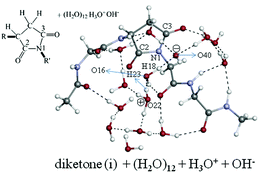
An isomerization reaction of a tetra-![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O)–CH2–CH2–COOH and (H2O)m. The m = 2 stepwise path was found to be of the smallest activation free energy. On the basis of this result, the first isomerization path of the tetra-
O)–CH2–CH2–COOH and (H2O)m. The m = 2 stepwise path was found to be of the smallest activation free energy. On the basis of this result, the first isomerization path of the tetra-

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...