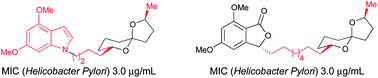
Abstract
Helicobacter pylori affects a significant proportion of the human population. It is the primary agent responsible for gastric and duodenal ulcers and has been further linked with gastric cancer and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT lymphoma). Eradication of H. pylori can cure these diseases; however the current therapies used are far from ideal. (+)-Spirolaxine methyl ether (2) exhibits potent activity against H. pylori and is therefore a promising drug candidate. Herein we report the synthesis of eight analogues of spirolaxine methyl ether (2), as well as their anti-H. pylori activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...