Frequency discretization in dielectrophoretic assisted cell sorting arrays to isolate neural cells†‡
Abstract
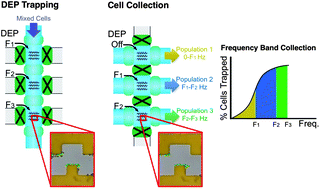
We present an automated dielectrophoretic assisted cell sorting (DACS) device for dielectric characterization and isolation of neural cells. Dielectrophoretic (DEP) principles are often used to develop cell sorting techniques. Here we report the first statistically significant neuronal sorting using DACS to enrich neurons from a heterogeneous population of mouse derived neural stem/progenitor cells (NSPCs) and neurons. We also study the dielectric dispersions within a heterogeneous cell population using a Monte-Carlo (MC) simulation. This simulation model explains the trapping behavior of populations as a function of frequency and predicts sorting efficiencies. The platform consists of a DEP electrode array with three multiplexed trapping regions that can be independently activated at different frequencies. A novel microfluidic manifold enables cell sorting by trapping and collecting cells at discrete frequency bands rather than single frequencies. The device is used to first determine the percentage of cells trapped at these frequency bands. With this characterization and the MC simulation we choose the optimal parameters for neuronal sorting. Cell sorting experiments presented achieve a 1.4-fold neuronal enrichment as predicted by our model.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Focus on USA

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...