Endosomal pH-activatable magnetic nanoparticle-capped mesoporous silica for intracellular controlled release†
Abstract
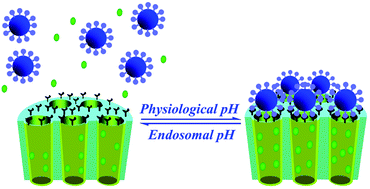
Endosomal pH-driven linkage-disintegration is a promising strategy to achieve intracellular delivery and controlled drug release. In this paper, a rapid endosomal pH-sensitive MSNs ensemble (i.e., MCM-TAA-Fe3O4) with magnetic nanoparticle caps was developed by anchoring superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles on the pore openings with an acid-labile substituted 1,3,5-triazaadamantane (TAA) group. The functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles served as a nanogate to regulate the release pattern and/or dosage of payload. The in vitro release experiment with model dexamethasone showed that the MCM-TAA-Fe3O4 ensembles exhibited quick release at pH 5.0–6.0 and zero release in physiological environment (pH = 7.4). Demonstrated with a MC3T3-E1 model cell line, this hybrid nanomaterial could successfully be endocytosed into cells and then release the encapsulated exogenous cargos into the cytosol. The new rapid endosomal pH-sensitive Fe3O4-capped-MSNs could serve as efficient carriers for intracellular controlled release of therapeutic agents in live cells, and may be potentially applied in clinical disease therapy, especially therapeutics and the metabolic manipulation of cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...