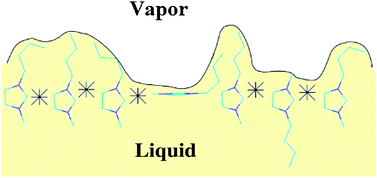
In this paper, we apply novel intrinsic analysis methods, coupled with bivariate orientation analysis, to obtain a detailed picture of the molecular-level structure of ionic liquid surfaces. We observe pronounced layering at the interface, alternating non-polar with ionic regions. The outermost regions of the surface are populated by alkyl chains, which are followed by a dense and tightly packed layer formed of oppositely charged ionic moieties. We then systematically change the cation chain length, the anion size, the temperature and the molecular model, to examine the effect of each of these parameters on the interfacial structure. Increasing the cation chain length promotes orientations in which the chain is pointing into the vapor, thus increasing the coverage of the surface with alkyl groups. Larger anions promote a disruption of the dense ionic layer, increasing the orientational freedom of cations and increasing the amount of free space. The temperature had a relatively small effect on the surface structure, while the effect of the choice of molecular model was clearly significant, particularly on the orientational preferences at the interface. Our study demonstrates the usefulness of molecular simulation methods in the design of ionic liquids to suit particular applications.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...