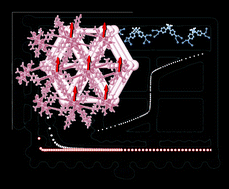
Five novel metal organic frameworks, belonging to three structural types, have been obtained hydrothermally. Three of them, with formula [M3(hfipbb)2(OH)2(H2O)] (M = Mn, Co, Ni; hfipbb = 4,4′-(hexafluoroisopropylidene)bis(benzoate) dianion) belong to the first structural type. The crystal structure of the Mn-based compound was obtained from single crystal synchrotron X-ray diffraction data, while the isostructural compounds of Co and Ni were studied by means of Rietveld analysis using powder X-ray diffraction data. The magnetic behavior of the compounds with M = Co and Ni is characterized by the onset of long-range ferromagnetic order at very low temperature with Curie temperatures near 8 and 2.5 K, respectively. Such spontaneous magnetization seems to be preceded by low-dimensional magnetic interactions, due to the nature of the secondary building units (SBUs) of the structure, which are triple chains built by M3O14 units. Structural and topological analyses of [Mn2(hfipbb)2(H2hfipbb)] and [Co2(hfipbb)2(H2hfipbb)] (2 and 3 structural types, respectively; H2hfipbb = 4,4′-(hexafluoroisopropylidene)bis(benzoic acid)) demonstrate that the packing of the rod-shaped SBUs in 2 prevents the framework interpenetration giving rise to a bnn net whereas 3 is a 2-fold interpenetrated pcu net with isolated paddle-wheel clusters as SBUs pcu. Concerning the magnetic behavior of 2 and 3, antiferromagnetic interactions observed at very low temperature (magnetic susceptibility maximum at 2.8 and 18 K, respectively) are confined to the secondary building units.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...