Electrochemically driven drug metabolism via cytochrome P450 2C9 isozyme microsomes with cytochrome P450 reductase and indium tin oxide nanoparticle composites†
Abstract
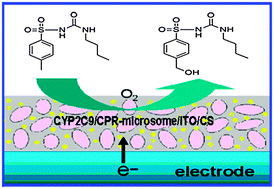
We describe herein an electrochemically driven drug metabolism strategy based on nanocomposites that integrate cyt P450 2C9 (CYP2C9) isozyme microsomes with cyt P450 reductase (CPR), indium tin oxide (ITO) nanoparticles and chitosan (CS). This novel bioelectronic system enables monitoring of the drug metabolism and enzyme inhibition.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...