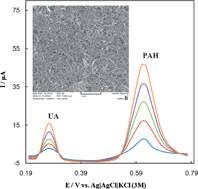
In the present study, for the first time, a simple and rapid electrochemical sensor was developed for the simultaneous determination of 4-aminohippuric acid (PAH) and uric acid (UA), based on the excellent properties of functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes (fMWCNTs). A glassy carbon electrode was modified via drop casting the suspension of fMWCNT onto its surface and then the modified electrode was used for the measurement. The electrochemical response characteristics of the modified electrode toward PAH and UA were investigated using cyclic voltammetry, differential pulse voltammetry and chronoamperometry. The values of transfer coefficient for oxidation of PAH and UA were calculated using electrochemical approaches and were found to be 0.43 and 0.46, respectively. PAH and UA in a mixture can be measured individually and simultaneously by differential pulse voltammetry. At the optimum pH of 6.0 in 0.1 M phosphate buffer solution, differential pulse voltammograms increase linearly with PAH and UA concentrations over the concentration ranges of 10–1000 μM of PAH and 1–100 μM of UA. The detection limits for PAH and UA were found to be 7.82 μM and 0.96 μM, respectively. The proposed method was also successfully applied to the determination of PAH and UA in real samples.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...