Graphene oxide integrated sensor for electrochemical monitoring of mitomycin C–DNA interaction†
Abstract
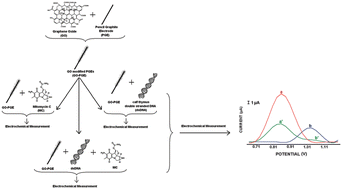
We present a graphene oxide (GO) integrated disposable electrochemical sensor for the enhanced detection of nucleic acids and the sensitive monitoring of the surface-confined interactions between the anticancer

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...