Thin films of substituted polyanilines: interactions with biomolecular systems†
Abstract
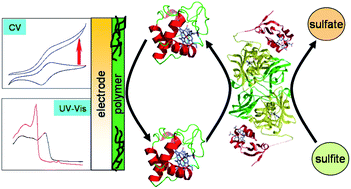
We use substituted polyanilines for the construction of new polymer electrodes for interaction studies with the redox protein cytochrome c (cyt c) and the enzyme sulfite oxidase (SO). For these purposes four different polyaniline copolymers are chemically synthesized. Three of them are copolymers, containing 2-methoxyaniline-5-sulfonic acid with variable ratios of aniline; the fourth copolymer consists of 3-amino-benzoic acid and aniline. The results show that all polymers are suitable for being immobilized as thin stable films on gold wire and indium tin oxide (ITO) electrode surfaces from DMSO solution. This can be demonstrated by cyclic voltammetry and UV-Vis spectroscopy measurements. Moreover, cyt c can be electrochemically detected not only in solution, but also immobilized on top of the polymer films. Furthermore, the appearance of a significant catalytic current has been demonstrated for the sulfonated polyanilines, when the polymer-coated protein electrode is being measured upon addition of sulfite oxidase, confirming the establishment of a bioanalytical signal chain. Best results have been obtained for the polymer with highest sulfonation grade. The redox switching of the polymer by the enzymatic reaction can also be analyzed by following the spectral properties of the polymer electrode.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...