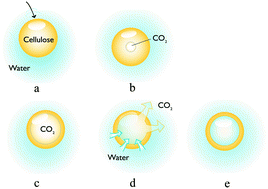
A new material consisting of mm-sized hollow cellulose spheres, for biomedical applications or for the preparation of low weight porous materials has been prepared by a unique solution precipitation (SP) method. The technique is based on three separate steps. In the first step, high molecular mass, non-modified cellulose is dissolved in a suitable solvent. This cellulose solution is then saturated with a suitable gas (CO2 or N2 in the present work) and finally this gas-saturated solution is drop-wise added to a water reservoir. In this step, the cellulose is precipitated and a gas bubble is nucleated in the center of the cellulose sphere. When stored in water, the hollow center is filled with water, indicating that the capsule wall is porous in nature. This was also supported by BET-area measurements as well as by high resolution SEM-images of broken capsule walls. The internal void volume of a capsule was about 5 μl and the wall volume was about 8 μl. It was also established that the properties of the cellulose capsules, i.e. wall and void volume, the specific surface area, the average pore size of the capsule wall, the wall density, and the compressive load capacity could be tuned by the choice of cellulose concentration in the solution before precipitation. The capsule wall volume and void volume were also affected by the choice of gas, the gas pressure and the gas dissolution time during the gas saturation step. The response of the cellulose wall of the prepared capsules to changes in pH and ion concentration in the surrounding solution was also investigated. The swelling–shrinking behavior was further investigated by introducing more charges to the capsule wall, via carboxymethylation of the cellulose. This was achieved by using carboxymethylated cellulose which increased the swelling–shrinking effect. The results show a typical polyelectrolyte gel behavior of the capsule wall and the wet modulus of the cellulose wall was determined to be between 0.09–0.2 MPa depending on the charge of the cellulose in the capsule wall. Furthermore, the freeze dried cellulose spheres had a modulus of 1.9–7.4 MPa, depending on the cellulose concentration during the preparation of the spheres. These cellulose capsules are suitable both for the preparation of porous materials, where these larger spheres are joined together in 3D-shaped materials, and for controlled release where the interior of the capsules is filled with active substances and these substances are released by controlling the pores in the capsule walls.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...