The muraminomicin biosynthetic gene cluster and enzymatic formation of the 2-deoxyaminoribosyl appendage†
Abstract
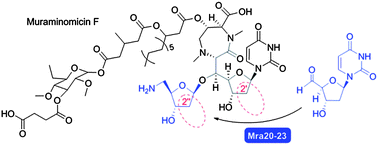
Muraminomicin is a lipopeptidyl
* Corresponding authors
a
Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY 40536, USA
E-mail:
svanlanen@uky.edu
Fax: +1 859 257 7564
Tel: +1 859 323 6271
b Biologics Research Laboratories, R&D Division, Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd., Tokyo 134-8630, Japan
c Natural Products Research Group, Discovery Science and Technology Department, Drug Discovery and Biomedical Technology Unit, Daiichi Sankyo RD Novare Co., Ltd., Tokyo 140-8710, Japan
d Biopharmaceutical Research Group I, Biopharmaceutical Technology Research Laboratories, Pharmaceutical Technology Division, Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd., Gunma, 370-0503 Japan
Muraminomicin is a lipopeptidyl

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
X. Chi, S. Baba, N. Tibrewal, M. Funabashi, K. Nonaka and S. G. Van Lanen, Med. Chem. Commun., 2013, 4, 239 DOI: 10.1039/C2MD20245J
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
